The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system. Every time you breathe, your lungs work hard to bring in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide — a vital exchange that keeps your body alive and functioning. Together, your lungs support nearly every cell in your body by fueling it with oxygen-rich blood.
What Are the Lungs?
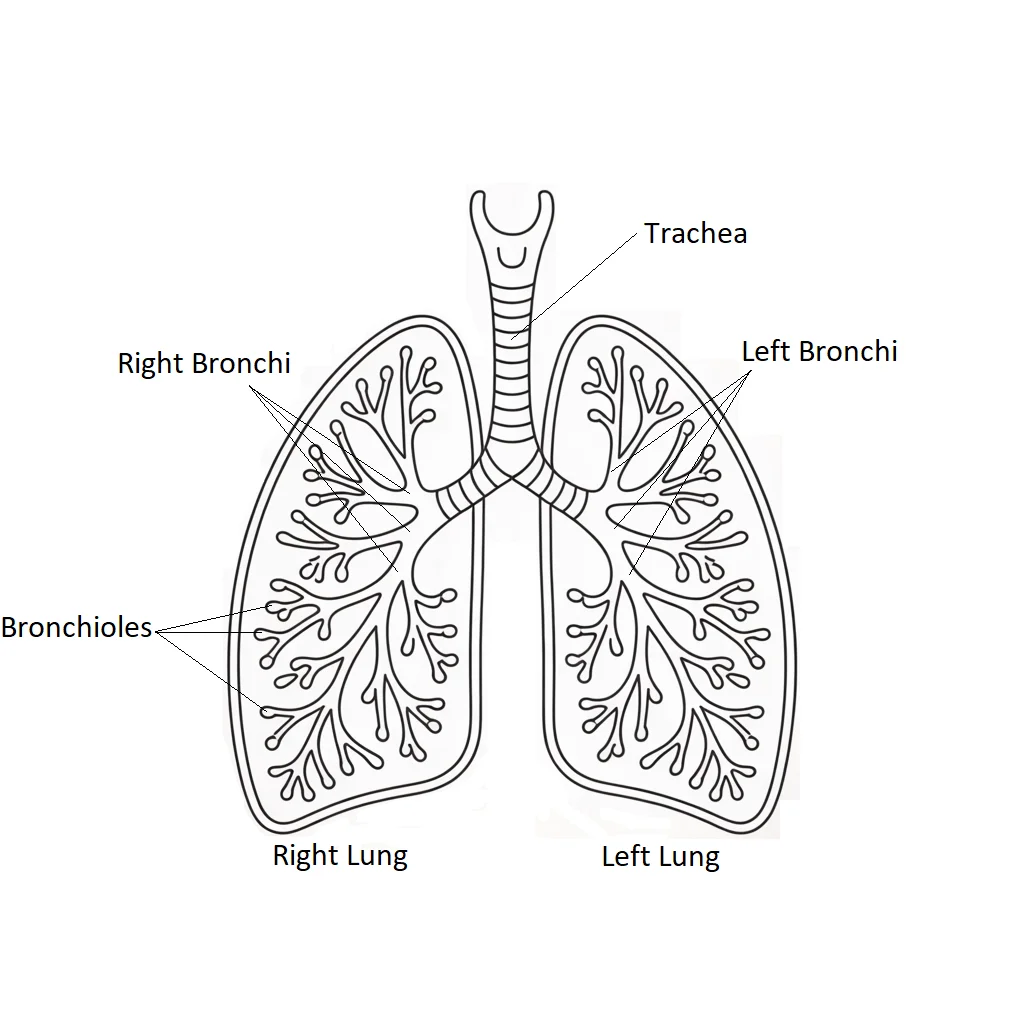
The lungs are a pair of spongy, air-filled organs located in your chest on either side of the heart. Protected by the ribcage, they are divided into lobes — the right lung has three lobes, and the left has two (to make space for the heart).
Air enters the body through the nose or mouth, travels down the trachea, branches into bronchi, then into smaller bronchioles, and finally reaches alveoli — tiny air sacs where gas exchange happens.
Main Functions
- Oxygenates blood: Delivers oxygen to the bloodstream via the alveoli.
- Removes carbon dioxide: Expels waste gas during exhalation.
- Regulates pH balance: Maintains blood’s acid-base levels.
- Filters air: Traps dust, microbes, and other particles.
- Supports vocalization: Works with the vocal cords to enable speech.
- Protects against infection: Contains immune cells that defend against airborne pathogens.
Anatomy Overview
| Part | Location/Feature | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Trachea | Windpipe connecting throat to lungs | Air passageway to lungs |
| Bronchi | Branches of the trachea | Direct air to left and right lungs |
| Bronchioles | Smaller branches of bronchi | Carry air deeper into the lungs |
| Alveoli | Tiny air sacs at bronchiole ends | Gas exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out) |
| Right Lung | Three lobes | Handles slightly more air volume |
| Left Lung | Two lobes (makes room for heart) | Slightly smaller than right lung |
| Diaphragm | Muscle beneath the lungs | Contracts to enable breathing |
Common Issues of the Lungs
Respiratory conditions range from temporary infections to chronic and life-threatening diseases. Common lung issues include:
- Asthma
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Pneumonia
- Tuberculosis
- Lung cancer
- Pulmonary embolism
- Bronchitis
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- COVID-19-related complications
Warning Signs to Watch For:
- Shortness of breath (especially at rest)
- Persistent cough or wheezing
- Chest tightness or pain
- Coughing up blood
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Chronic fatigue or weakness
- Bluish lips or fingernails (lack of oxygen)
Best Practices for Healthy Lungs
Your lungs are durable but vulnerable to environmental factors. Keep them healthy by following these tips:
- Don’t smoke: Tobacco is the leading cause of lung disease, including cancer and COPD.
- Avoid air pollution: Use masks in polluted areas and avoid secondhand smoke.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity strengthens lung capacity.
- Practice deep breathing: Helps improve oxygen intake and lung efficiency.
- Get vaccinated: Flu, pneumonia, and COVID-19 vaccines help prevent respiratory infections.
- Monitor indoor air quality: Use air purifiers and reduce mold, dust, and chemical exposure.
- Protect against occupational hazards: Wear protective gear if exposed to dust, fumes, or chemicals.
When Should You Consult a Doctor?
Seek medical advice if you notice:
- Persistent or unexplained shortness of breath
- Chest pain while breathing
- Ongoing cough lasting more than 3 weeks
- Sudden breathing difficulty
- Wheezing or noisy breathing
- Coughing up blood or mucus
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent serious complications and improve outcomes in most lung conditions.
Conclusion
Your lungs are your body’s oxygen powerhouse. They work around the clock to fuel every system and cell. Keeping your lungs healthy — through clean air, active living, and routine screenings — is one of the most important steps you can take toward long-term wellness.
At DNA Labs India, we offer advanced respiratory health tests, including lung function analysis and genetic screening for inherited respiratory conditions.
Contact DNA Labs India today for personalized lung health assessments and early diagnosis support.
✅ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the main function of the lungs?
A: The lungs bring oxygen into the body and remove carbon dioxide from the blood through a process called gas exchange, which occurs in the alveoli.
Q2: How many lungs do we have and are they the same size?
A: Humans have two lungs. The right lung has three lobes and is slightly larger, while the left lung has two lobes to accommodate the heart.
Q3: What are common signs of lung problems?
A: Symptoms include shortness of breath, chronic cough, wheezing, chest pain, fatigue, and coughing up blood or mucus.
Q4: Can lung tissue regenerate?
A: Unlike the liver, the lungs have limited regenerative capacity. Some healing is possible after injury or mild inflammation, but chronic damage like in COPD or fibrosis is often irreversible.
Q5: How can I keep my lungs healthy?
A: Avoid smoking, stay active, maintain good indoor air quality, get vaccinated, and protect yourself from pollutants and respiratory infections.
Q6: What tests check lung health?
A: Common lung function tests include spirometry, peak flow tests, chest X-rays, CT scans, and arterial blood gas analysis.
Q7: Is shortness of breath always a sign of lung disease?
A: Not always. It can also be related to heart conditions, anxiety, anemia, or physical deconditioning. However, persistent symptoms should be checked by a doctor.


