What Are Organs?
Organs are specialized structures in the human body that perform specific, essential functions required for survival and well-being. Each organ is composed of multiple tissue types working together to support vital biological processes such as circulation, digestion, respiration, and waste removal. Organs do not function in isolation—they operate as part of larger systems like the nervous, digestive, or respiratory systems. For example, the heart pumps blood, the lungs exchange oxygen, and the liver processes toxins. These interconnected roles make organs fundamental to maintaining life and health. Understanding how organs function individually and collectively provides a deeper insight into the complexity and resilience of the human body.
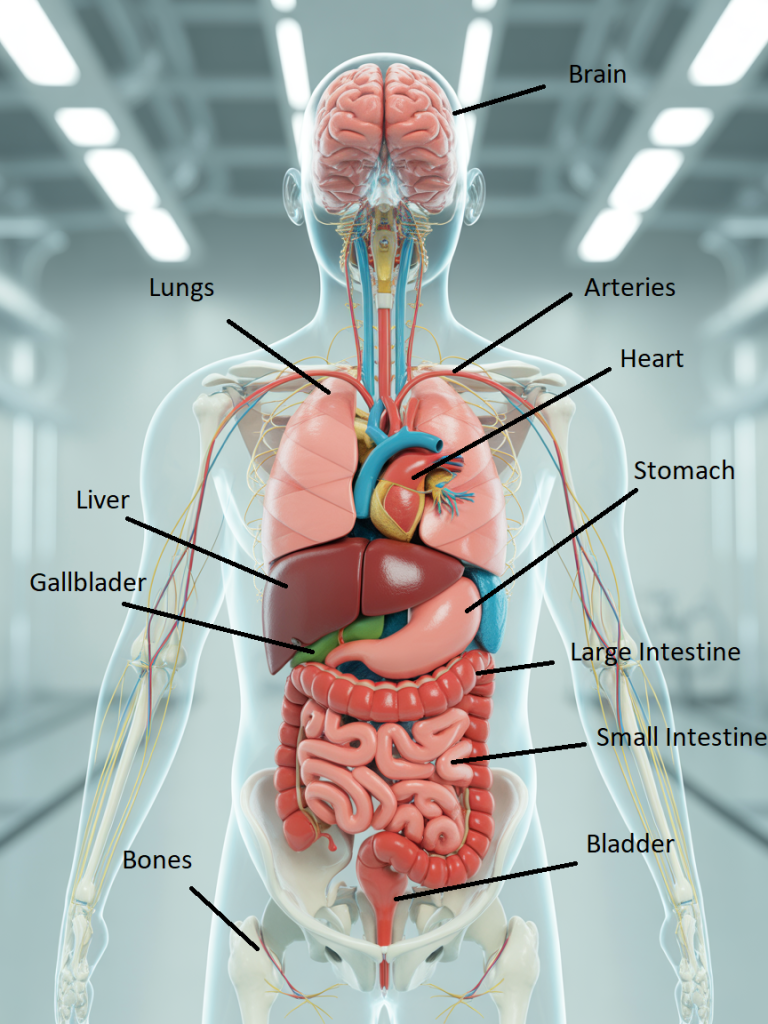
Types of Organs in the Human Body
1. Vital Organs
Vital organs are absolutely essential for survival. Without them, life is not possible.
- Brain – Controls the nervous system and bodily functions.
- Heart – Pumps blood to deliver oxygen and nutrients.
- Lungs – Allow breathing and oxygen exchange.
- Liver – Processes toxins, aids in digestion, and stores energy.
- Kidneys – Filter blood and regulate fluid balance.
2. Major Organs
These organs, while not always “vital,” are key to proper body function and health.
- Stomach – Breaks down food using acids and enzymes.
- Small and Large Intestines – Absorb nutrients and remove waste.
- Pancreas – Regulates blood sugar and aids digestion.
- Spleen – Supports immune function and filters blood.
- Bladder – Stores urine for elimination.
- Skin – The body’s largest organ, protecting against harm and regulating temperature.
3. Sensory Organs
These organs help you experience and react to the world.
- Eyes – Enable vision.
- Ears – Allow hearing and balance.
- Nose – Detects smells and filters air.
- Tongue – Detects taste and assists in speaking.
- Skin – Senses touch, pressure, temperature, and pain.
Functions of Organs
Each organ in the body has a unique job. Organs support:
- Circulation of blood and oxygen
- Digestion of food
- Removal of waste
- Immune defense
- Hormone production
- Sensory perception
Organs rarely work alone. Instead, they form part of body systems — groups of organs working together to perform major bodily functions.
Organ Systems of the Human Body
Here are the main organ systems and the organs they include:
- Circulatory System – Heart, blood vessels
- Respiratory System – Lungs, trachea, nose
- Digestive System – Mouth, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas
- Urinary System – Kidneys, bladder, urethra
- Nervous System – Brain, spinal cord, nerves
- Endocrine System – Glands (thyroid, pancreas, adrenal)
- Reproductive System – Ovaries, uterus, testes
- Integumentary System – Skin, hair, nails
- Lymphatic/Immune System – Spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils
Can Humans Live Without Certain Organs?
Yes, humans can survive without some organs — often with medical or surgical help.
You can live without:
- One kidney
- One lung
- Spleen
- Gallbladder
- Appendix
- Reproductive organs
- Stomach (partially or fully)
- Colon (with modifications)
However, organs like the brain, heart, liver, and both kidneys are considered vital — you cannot survive without them for long.
Interesting Facts About Organs
- The skin is the body’s largest organ.
- The liver can regenerate up to 75% of its tissue.
- You only need one kidney to live a healthy life.
- The small intestine is about 20 feet long — longer than the large intestine.
- The heart beats around 100,000 times per day.
Conclusion
Organs are the life-sustaining machinery of the human body. From the brain and heart to the lungs and liver, each plays a role in keeping us alive, healthy, and functioning. Understanding how organs work helps us appreciate the complexity and resilience of the human body. Whether you’re a student, teacher, or curious reader, knowing about your organs is the first step toward understanding how your body truly works.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the largest organ in the human body?
A: The skin is the largest organ. It protects the body, regulates temperature, and senses touch.
Q2: Can a person live without a kidney?
A: Yes, people can live with just one healthy kidney because it can filter blood efficiently on its own.
Q3: What organs are considered vital for survival?
A: The brain, heart, lungs, liver, and kidneys are vital organs necessary for life.
Q4: Is the appendix an organ?
A: The appendix is considered a vestigial organ. It has some immune functions but is not essential and can be removed safely.
Q5: How do organs work together in the body?
A: Organs are part of organ systems that coordinate to perform complex functions like digestion, circulation, and respiration.
Q6: Can organs regenerate after injury?
A: Some organs, like the liver, can regenerate damaged tissue, but many others have limited regenerative ability.